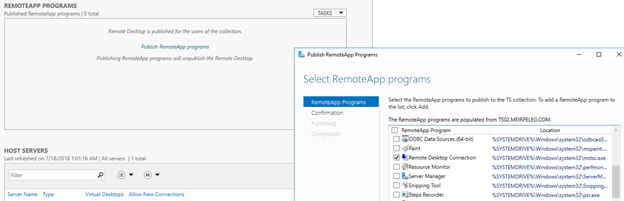
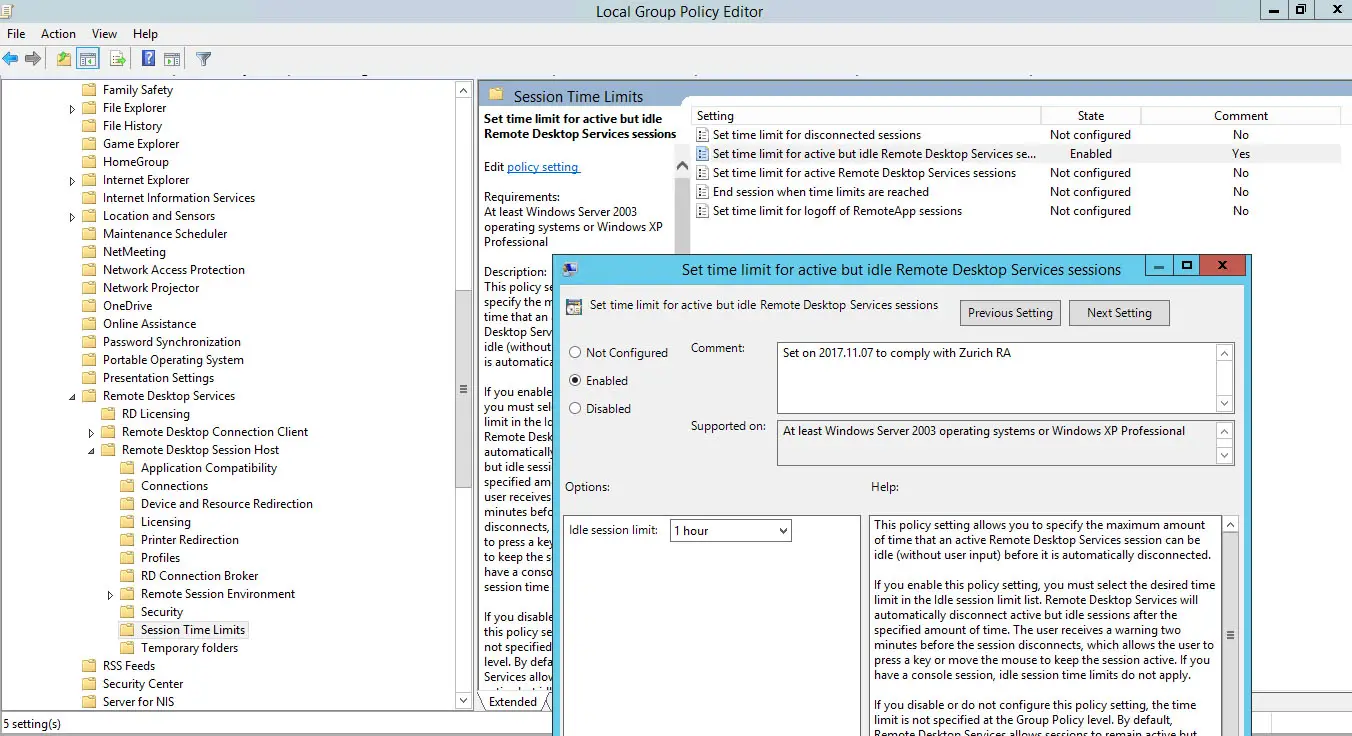
- Enable Remote Desktop Server 2016
- Windows Server
- Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Access Denied
- Windows Server 2016 Remote Access Role
- Remote Access To Windows Server
- Enable Rdp On Server 2016

Mar 09, 2020 Go to Server Manager in Windows Server 2016. Click Add Roles and Features. Then select Role-based or feature-based installation. Choose: Remote Desktop Services. Then choose: Remote Desktop Session Host. Install the role. Run GDPEdit.msc (use the search feature on Windows 2016 server by clicking the magnifying glass). You can use Remote Access to route network traffic between subnets on your Local Area Network. Routing provides support for Network Address Translation (NAT) routers, LAN routers running BGP, Routing Information Protocol (RIP), and multicast-capable routers using Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP). As a full-featured router, you can deploy RAS on either a server computer or as a virtual machine (VM. 1 Client PC running Windows 10 (CLIENT-10) 01 – open Server Manager Click Add roles and features. 02 – Click Next to proceed. 03 – Choose Remote Desktop Services installation button and click next to proceed. 04 – on the Select deployment type box, click Quick Start (I choose this because I only have One Server for RDS and Remote Apps). We use remote WMI checks to monitor out Server 2012 machines and all works fine. We set up a new user and make it a local administrator, then deny log on locally and via RDP in the local security policy and use this account for WMI checks. I've just tried to do the same on a new Server 2016 machine and I keep getting acces denied when querying WMI.
-->Applies To: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016
This topic describes how to configure the client and server settings that are required for remote management of DirectAccess clients. Before you begin the deployment steps, ensure that you have completed the planning steps that are described in Step 2 Plan the Remote Access Deployment.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Install the Remote Access role | Install the Remote Access role. |
| Configure the deployment type | Configure the deployment type as DirectAccess and VPN, DirectAccess only, or VPN only. |
| Configure DirectAccess clients | Configure the Remote Access server with the security groups that contain DirectAccess clients. |
| Configure the Remote Access server | Configure the Remote Access server settings. |
| Configure the infrastructure servers | Configure the infrastructure servers that are used in the organization. |
| Configure application servers | Configure the application servers to require authentication and encryption. |
| Configuration summary and alternate GPOs | View the Remote Access configuration summary, and modify the GPOs if desired. |
Note
This topic includes sample Windows PowerShell cmdlets that you can use to automate some of the procedures described. For more information, see Using Cmdlets.
Install the Remote Access role
You must install the Remote Access role on a server in your organization that will act as the Remote Access server.
To install the Remote Access role
To install the Remote Access role on DirectAccess servers
On the DirectAccess server, in the Server Manager console, in the Dashboard, click Add roles and features.
Click Next three times to get to the server role selection screen.
On the Select Server Roles dialog, select Remote Access, and then click Next.
Click Next three times.
On the Select role services dialog, select DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) and then click Add Features.
Select Routing, select Web Application Proxy, click Add Features, and then click Next.
Click Next, and then click Install.
On the Installation progress dialog, verify that the installation was successful, and then click Close.
Windows PowerShell equivalent commands
The following Windows PowerShell cmdlet or cmdlets perform the same function as the preceding procedure. Enter each cmdlet on a single line, even though they may appear word-wrapped across several lines here because of formatting constraints.
Configure the deployment type
There are three options that you can use to deploy Remote Access from the Remote Access Management console:
DirectAccess and VPN
DirectAccess only
VPN only
Note
This guide uses the DirectAccess only method of deployment in the example procedures.
To configure the deployment type
On the Remote Access server, open the Remote Access Management console: On the Start screen, type, type Remote Access Management Console, and then press ENTER. If the User Account Control dialog box appears, confirm that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Yes.
In the Remote Access Management Console, in the middle pane, click Run the Remote Access Setup Wizard.
In the Configure Remote Access dialog box, select DirectAccess and VPN, DirectAccess only, or VPN only.
Configure DirectAccess clients
For a client computer to be provisioned to use DirectAccess, it must belong to the selected security group. After DirectAccess is configured, client computers in the security group are provisioned to receive the DirectAccess Group Policy Objects (GPOs) for remote management.
To configure DirectAccess clients
In the middle pane of the Remote Access Management console, in the Step 1 Remote Clients area, click Configure.
In the DirectAccess Client Setup Wizard, on the Deployment Scenario page, click Deploy DirectAccess for remote management only, and then click Next.
On the Select Groups page, click Add.
In the Select Groups dialog box, select the security groups that contain the DirectAccess client computers, and then click Next.
On the Network Connectivity Assistant page:
In the table, add the resources that will be used to determine connectivity to the internal network. A default web probe is created automatically if no other resources are configured. When configuring the web probe locations for determining connectivity to the enterprise network, ensure that you have at least one HTTP based probe configured. Configuring only a ping probe is not sufficient, and it could lead to an inaccurate determination of connectivity status. This is because ping is exempted from IPsec. As a result, ping does not ensure that the IPsec tunnels are properly established.
Add a Help Desk email address to allow users to send information if they experience connectivity issues.
Provide a friendly name for the DirectAccess connection.
Select the Allow DirectAccess clients to use local name resolution check box, if required.
Note
When local name resolution is enabled, users who are running the NCA can resolve names by using DNS servers that are configured on the DirectAccess client computer.
Click Finish.
Configure the Remote Access server
To deploy Remote Access, you need to configure the server that will act as the Remote Access server with the following:
Correct network adapters
A public URL for the Remote Access server to which client computers can connect (the ConnectTo address)
An IP-HTTPS certificate with a subject that matches the ConnectTo address
IPv6 settings
Client computer authentication
To configure the Remote Access server
In the middle pane of the Remote Access Management console, in the Step 2 Remote Access Server area, click Configure.
In the Remote Access Server Setup Wizard, on the Network Topology page, click the deployment topology that will be used in your organization. In Type the public name or IPv4 address used by clients to connect to the Remote Access server, enter the public name for the deployment (this name matches the subject name of the IP-HTTPS certificate, for example, edge1.contoso.com), and then click Next.
On the Network Adapters page, the wizard automatically detects:
Network adapters for the networks in your deployment. If the wizard does not detect the correct network adapters, manually select the correct adapters.
IP-HTTPS certificate. This is based on the public name for the deployment that you set during the previous step of the wizard. If the wizard does not detect the correct IP-HTTPS certificate, click Browse to manually select the correct certificate.
Click Next.
On the Prefix Configuration page (this page is only visible if IPv6 is detected in the internal network), the wizard automatically detects the IPv6 settings that are used on the internal network. If your deployment requires additional prefixes, configure the IPv6 prefixes for the internal network, an IPv6 prefix to assign to DirectAccess client computers, and an IPv6 prefix to assign to VPN client computers.
On the Authentication page:
For multisite and two-factor authentication deployments, you must use computer certificate authentication. Select the Use computer certificates check box to use computer certificate authentication and select the IPsec root certificate.
To enable client computers running Windows 7 to connect via DirectAccess, select the Enable Windows 7 client computers to connect via DirectAccess check box. You must also use computer certificate authentication in this type of deployment.
Click Finish.
Configure the infrastructure servers
To configure the infrastructure servers in a Remote Access deployment, you must configure the following:
Network location server
DNS settings, including the DNS suffix search list
Any management servers that are not automatically detected by Remote Access
To configure the infrastructure servers
In the middle pane of the Remote Access Management console, in the Step 3 Infrastructure Servers area, click Configure.
In the Infrastructure Server Setup Wizard, on the Network Location Server page, click the option that corresponds to the location of the network location server in your deployment.
If the network location server is on a remote web server, enter the URL, and then click Validate before you continue.
If the network location server is on the Remote Access server, click Browse to locate the relevant certificate, and then click Next.
On the DNS page, in the table, enter additional name suffixes that will be applied as Name Resolution Policy Table (NRPT) exemptions. Select a local name resolution option, and then click Next.
On the DNS Suffix Search List page, the Remote Access server automatically detects domain suffixes in the deployment. Use the Add and Remove buttons to create the list of domain suffixes that you want to use. To add a new domain suffix, in New Suffix, enter the suffix, and then click Add. Click Next.
On the Management page, add management servers that are not detected automatically, and then click Next. Remote Access automatically adds domain controllers and Configuration Manager servers.
Click Finish.
Configure application servers
In a full Remote Access deployment, configuring application servers is an optional task. In this scenario for remote management of DirectAccess clients, application servers are not utilized and this step is greyed out to indicate that it is not active. Click Finish to apply the configuration.
Configuration summary and alternate GPOs
When the Remote Access configuration is complete, the Remote Access Review is displayed. You can review all of the settings that you previously selected, including:
GPO Settings
The DirectAccess server GPO name and Client GPO name are listed. You can click the Change link next to the GPO Settings heading to modify the GPO settings.
Remote Clients
The DirectAccess client configuration is displayed, including the security group, connectivity verifiers, and DirectAccess connection name.
Remote Access Server
The DirectAccess configuration is displayed, including the public name and address, network adapter configuration, and certificate information.
Infrastructure Servers
This list includes the network location server URL, DNS suffixes that are used by DirectAccess clients, and management server information.
See also
-->Applies To: Windows Server 2016 Essentials, Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials, Windows Server 2012 Essentials
Remote Web Access in Windows Server Essentials, or in Windows Server 2012 R2 with the Windows Server Essentials Experience role installed, provides a streamlined, touch-friendly browser experience for accessing applications and data from virtually anywhere that you have an Internet connection and by using almost any device. To use the Remote Web Access functionality, you must first turn it on by using the Set Up Anywhere Access Wizard, and then set up your router and domain name.
In this topic
Turn on and configure Remote Web Access
The following topics will help you turn on and configure Remote Web Access:
Remote Web Access overview
When you are away from your office, you can open a web browser and access Remote Web Access from anywhere that has Internet access. In Remote Web Access, you can:
Access shared files and folders on the server.
Access your server and computers on the network. This means that you can access the desktop of a networked computer as if you were sitting in front of it at your office.
Remote Web Access is not turned on by default. When you run the Set up Anywhere Access Wizard, the wizard attempts to set up your router and Internet connectivity. After Remote Web Access is turned on, you can set up a domain name for your server and customize Remote Web Access. You can also set up the router again if you change your router.
Permission to access Remote Web Access is not automatically granted when you add a new user account. When you add a user account, you can choose to allow access to shared folders, the Media Library, computers, Home page links, and the server Dashboard. You can also specify that a user not be allowed to use Remote Web Access.
The Remote Web Access setting is displayed for each user account on the USERS tab of the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard. To change the Remote Web Access setting, right-click the user account, and then click View the account properties.
Turn on Remote Web Access
You can turn on Remote Web Access by running the Set up Anywhere Access Wizard from the server Dashboard.
To turn on Remote Web Access
Open the Dashboard.
Click Settings, and then click the Anywhere Access tab.
Click Configure. The Set Up Anywhere Access Wizard appears.
On the Choose Anywhere Access features to enable page, select the Remote Web Access check box.
Follow the instructions to complete the wizard.
Change your region
You must be a network administrator to change the region setting in Windows Server Essentials.
To change the region setting
On a computer that is connected to Windows Server Essentials, open the Dashboard.
Click Settings.
On the General tab, click the drop-down list in the Country/Region location of server section.
From the drop-down list, select the new region, and then click Apply to accept the new region setting.
Manage Remote Web Access permissions
When you add a user account in Windows Server Essentials, the new user is allowed by default to use Remote Web Access. If you chose not to allow Remote Web Access for a user account, and then find that the user needs to use Remote Web Access, you can update the user account's properties.
To manage Remote Web Access permissions for a user account
Log on to the Dashboard, and then click Users.
Click the user account that you want to manage, and then click View the account properties in the Tasks pane.
In the Properties dialog box, click the Anywhere Access tab.
On the Anywhere Access tab, select the Allow Remote Web Access and access to web services applications check box to allow a user to connect to the server using Remote Web Access.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
For more information, see Manage User Accounts.
Secure Remote Web Access
Windows Server Essentials uses a security certificate to help secure the information that is exchanged between the software and a web browser. When you install the Connector software on your computers, the security certificate for Windows Server Essentials is added to the trusted certificate list on your computers. The best way for users to access Remote Web Access when they are away from your office is to use a portable computer that has the Connector software installed on it.
Warning
Users who use Remote Web Access from public locations or other untrusted computers should ensure that they log off the website before leaving the computer unattended or when they are finished with their session.
Manage Remote Web Access and VPN users
You can use VPN to connect to Windows Server Essentials and access all your resources that are stored on the server. This is especially useful if you have a client computer that is set up with network accounts that can be used to connect to a hosted Windows Server Essentials server through a VPN connection. All the newly created user accounts on the hosted Windows Server Essentials server must use VPN to log on to the client computer for the first time.
To set VPN and Remote Web Access permissions for network users
Open the Dashboard.
On the navigation bar, click USERS.
In the list of user accounts, select the user account that you want to grant permissions to access the desktop remotely.
In the <User Account> Tasks pane, click Properties.
In <User Account> Properties, click the Anywhere Access tab.
On the Anywhere Access tab, do the following:
To allow a user to connect to the server by using VPN, select the Allow Virtual Private Network (VPN) check box.
To allow a user to connect to the server by using Remote Web Access, select the Allow Remote Web Access and access to web services applications check box.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
Set up your router
When you configure your server for Remote Web Access, the Set Up Anywhere Access Wizard attempts to set up the router. If you change routers or change settings on the router, you must rerun the Set Up Your Router Wizard. For more information, see the following topics:
Set up your router
During this step, Windows Server Essentials attempts to automatically configure your router by using UPnP commands. To do this, your router must support UPnP standards, and the UPnP setting must be enabled on your router.
Note

Your network configuration should follow the supported network requirements for Windows Server Essentials. There should be only one router on your network.
If the router is not set up by the Set Up Your Domain Name Wizard, you must manually forward port 443. For information about how to set up port forwarding on your router, see the Small Business Server forum.
Replace a router
Replace the router according to the manufacturer's instructions, and then run the Set Up Your Router Wizard to configure the new router.
To set up your new router
On the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard, click Settings.
Click the Anywhere Access tab, and then in the Router section, click Set up. The Set Up Your Router Wizard starts.
Follow the instructions in the wizard to finish setting up your new router.
Network location defined
A network location is a collection of network settings that Windows applies when you connect to a network. The settings vary and can be customized based on the type of network that you use. The settings for a network location determine whether certain features (such as file and printer sharing, network discovery, and public folder sharing) are turned on or off. Network locations are useful when you need to connect to different networks.
As an example, you may own a laptop computer that you use at home and on the job. When you are in the office, you connect to the office network. However, when you come home, you use your laptop to access and play videos and music that is stored on the home server. When you connect to a new network and specify the location type, Windows assigns a network profile that is preset for that type of location. The next time you connect to that network, Windows recognizes the network and automatically assigns the correct settings. This adds a layer of security to help protect the information on your computer, and only the network features that you need for that location are turned on.
There are four kinds of network locations:
Home network Choose this network for home networks or when you know and trust the people and devices on the network. Computers on a home network can belong to a home group. Network discovery is turned on for home networks, which allows you to see other computers and devices on the network and allows other network users to see your computer.
Work network Choose this network for small office or other workplace networks. Network discovery, which allows you to see other computers and devices on a network and allows other network users to see your computer, is on by default, but you cannot create or join a home group.
Public network Choose this network for public places (such as coffee shops or airports). This location is designed to keep your computer from being visible to other computers and to help protect your computer from malicious software from the Internet. Home group is not available on public networks, and network discovery is turned off. You should also choose this option if you're connected directly to the Internet without using a router, or if you have a mobile broadband connection.
Domain Choose this network for domains such as those at enterprise workplaces. This type of network location is controlled by your network administrator, and it cannot be selected or changed.
Enable Remote Desktop Services ActiveX controls
The Remote Desktop Services ActiveX controls allows you to access your home or business computer, via the Internet, from another computer by using Remote Web Access.
To enable Remote Desktop Services ActiveX controls
In Internet Explorer, click Tools, and then click Internet Options.
On the Security tab, click Custom level.
In the ActiveX controls and plug-ins section, do the following:
Under Download signed ActiveX controls, click Prompt.
Under Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins, click Enable.
Click OK twice to accept the changes and close the dialog box.
Set up your domain name
After Remote Web Access is turned on, you can set up a domain name for your server that is running Windows Server Essentials. This is a necessary step if you plan to use Remote Web Access from a remote computer. For more information, see the following topics:
Domain names overview
A domain name uniquely identifies your server on the Internet. Domain names consist of at least two parts: a top level domain name (TLD) and a second level domain name. For example, in contoso.com, com is the TLD and contoso is the second level domain name.
While you are away from your office, you can use your domain name to access shared files on the server or computers on the network. You can also manage your server when you are away. For example, you register contoso.com for your server. When you are away from your office, you can open a web browser on your laptop and type contoso.com in the address text box to connect to the instance of Remote Web Access that you set up on Windows Server Essentials.
Understand Microsoft personalized domain names
A Microsoft personalized domain name includes the following features:
A custom domain name for Remote Web Access (for example, yourhostname.remotewebaccess.com). Your domain name is associated with your public IP address.
A DNS dynamic update protocol service so that Remote Web Access using your domain name will not be interrupted if your public IP address changes. Typically, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) for your organization's broadband connections provide dynamic public IP addresses that can change.
A trusted certificate associated with the domain name.
To integrate a Microsoft personalized domain name with your server, you need a Microsoft account (formerly known as a Windows Live ID). If you do not have a Microsoft account, you can sign up for one at the Microsoft Hotmail website.
Important
Windows Live allows special characters in your Microsoft account password that the server does not support. If you use a Microsoft personalized domain, ensure that your Microsoft account password contains only characters that the server supports. The server does not support use of the characters $, /, ', and %.
Use a new or existing domain name
Enable Remote Desktop Server 2016
To automatically set up your domain name on a server running Windows Server Essentials, you must use a domain name service provider that is listed in the Set Up Your Domain Name Wizard. You may choose to get a new domain name or use an existing domain name. Do one of the following:
If you want to get a new domain name from one of the domain name service providers that are listed in the wizard, click I want to set up a new domain name.
If you have an existing domain name that you purchased from one of the supported domain name service providers, you can use the Set Up Your Domain Name Wizard to set up the domain name for your server. Click I want to use a domain name I already own, and then type the domain name in the Set Up Your Domain Name text box. You must provide the user name and password that you used to purchase the domain name.
If you have an existing domain name that you purchased from a domain name service provider that is not supported by Windows Server Essentials, and you want to use the Set Up Your Domain Name Wizard to set up the domain name for your server, you can transfer the domain name to one of the domain name service providers listed in the wizard. Click I want to use a domain name I already own, type the domain name in the Domain Name text box, and then follow the instructions on the domain name service provider's website to transfer the domain name.
Set up a domain name
When you turn on Remote Web Access, you can choose to set up the Internet domain name of the server.
To set up or manage an Internet domain name
Open the Dashboard.
Click Server settings, and then click the Anywhere Access tab.
In the Domain name section, click Set up.
Follow the instructions to complete the wizard. If you do not already own a domain name and certificate, the wizard helps you find a domain name provider to purchase a domain name and certificate, or you can get a personalized Microsoft domain name.
Choose a domain name service provider
You should choose a domain name service provider that supports the domain name extension that you want to use. The Set Up Your Domain Name Wizard includes a list of qualified providers that you can use with a link to each provider's website. Click the More Info link beside each provider's name to obtain information about the services and prices that are offered by the provider.
Note
Some domain name service providers serve broad international regions and others serve smaller markets. Because of this, some providers may not offer a website that is translated into your language of preference.
When you purchase your domain name, you might also consider purchasing the Domain Name System (DNS) dynamic update protocol service from your domain name service provider. DNS dynamic update protocol is a service that lets anyone on the Internet gain access to resources on a local network when the IP address of that network is constantly changing. Or you can purchase a static IP address from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to assure that your IP address does not change.
Choose a domain name
Choose a name that uniquely identifies your business server. For example, if your business name is Contoso Ltd, you might choose Contoso to uniquely identify your home or business server on the Internet. If the domain name is not available, try another variation of that name, or perhaps something completely different.
The name you type can contain the following:
63 characters maximum
Letters (English or your localized characters), numbers, or hyphens (-). The name must begin and end with a letter or a number.
Choose a domain name prefix
A domain name consists of hierarchical labels.
The top-level domain extension is the right-most label in the domain name. For example, in www.contoso.com, com is the top-level domain name extension.
The second-level domain name is the label next to the top-level domain name extension. The second-level domain name is often created based on the company name, products, or services. For example, in www.contoso.com, contoso is the second-level domain name and was chosen for the company name Contoso Pharmaceuticals. The second-level domain is sometimes referred to as the hostname, which has an IP address associated with it.
The domain name prefix identifies a subdomain. The subdomain name can be used to identify services, devices, or regions. For example, Contoso Pharmaceuticals wants to allow remote users to log on to Remote Web Access, but does not want the website to be available to the public, so they create a subdomain that allows only users with appropriate permissions to access the website. Contoso Pharmaceuticals sets up remote.contoso.com as the subdomain, and remote is the domain name prefix.
Tip
It is recommended that you use the default Remote as the prefix for your domain name.
Choose a domain name extension
When you choose a domain name for your Internet website, you also need to specify the domain name extension that you want to use. The extension is identified by the letters that follow the final period of any domain name. (The formal term for the extension is the top-level domain or TLD.)
There are two main types of domain extensions that you can use: generic and country-code.
Generic top-level domains
Generic domain extensions are three or more letters in length, and they are typically used by certain types of organizations.
Examples of generic top-level domains
| Domain Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| .com | Typically used by commercial organizations, but it can be used by anyone. |
| .net | Designed for businesses that offer network infrastructure services. |
| .org | Originally used by non-profit agencies and other business that did not fall into another generic top-level domain category. Can be used by anyone. |
| .edu | Restricted for use by educational organizations. |
Country-code top-level domains
These domain extensions are two letters in length. They are designed to be used by organizations in the country or region that is associated with that code. Some country-code top-level domains are restricted for use by citizens of that country or region. Others are available for use by anyone.
Examples of country-code top-level domains
| Domain Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| .ca | For use by websites in Canada |
| .cn | For use by websites in China |
| .de | For use by websites in Germany |
| .co.uk | For use by websites in the United Kingdom |
To view the complete list of top-level domains, see the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority website.
If a domain extension is not available to select in the Set Up Domain Name Wizard
When you run the Set Up Domain Name Wizard, the wizard looks at your system information to determine your country or region. The wizard then displays only those domain extensions that the participating providers in your area support. If the domain extension that you want does not appear in the list, you must choose a different domain extension to continue. Select an extension from the list that the wizard returned.
Update or upgrade your domain name service
You may need to update or upgrade your domain name service if you purchased a domain name, but did not purchase a certificate. You must have a certificate for your domain name from your domain name service provider.
Note
Work with your domain name service provider to determine the type of certificate that you need. The certificate can be one of the inexpensive certificates that are offered. However, you should review the documentation and features of higher level security certificates to determine if they better meet your business needs.
Export or import your certificate on your server
If you want to create a backup copy of a certificate or use it on another server, you must export the certificate. For information about exporting certificates, see Export a Certificate.
Set up a domain name manually
If you choose this option, the server does not monitor or maintain your domain name, and it does not alert you if there is a configuration issue. You might also consider this option if any of the following is true:
No partner domain name providers are listed for your country or region.
The partner domain providers listed do not support your domain name extension.
You have an existing domain name from a domain name provider that is not currently a partner, and you do not want to transfer that domain name to a Windows Server Essentials supported domain name provider.
The wizard does not list the domain name extension that you want to use, but the extension is available from a domain name provider that is not currently a partner.
If you choose to set up your domain name manually, work with your domain name service provider to create an A Record for your domain.
To create an A Record
Decide on a host name, such as remote. This is the domain name prefix. The domain name prefix plus your domain name will define the URL to open your Remote Web Access logon page; for example, http://remote.contoso.com.
In your domain name service providers configuration dashboard (usually on their webpage), create the A record for the host name that you decided on in Step 1. Ensure that the IP address that you specify in the A record is the IP address on the WAN side of your router (the Internet facing side). Consult your router documentation to find your WAN IP address.
It is recommended that you contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to purchase a static IP address for your network. This ensures that the IP address does not change and that your DNS entry does not become outdated.
If you do not have the option to obtain a static IP address from your ISP, you might also consider purchasing the Domain Name System (DNS) dynamic update protocol service from your domain name service provider or another service provider. DNS dynamic update protocol is a service that keeps the WAN IP address for your network up to date so that the IP address can be resolved to your domain name even if the IP address changes.
Import a trusted certificate when the wizard prompts you. If you do not have a trusted certificate, you can obtain one from one of the supported domain name providers listed in the wizard or purchase one from the trusted provider of your choice. For more information about a trusted certificate, contact your domain name provider.
Find your domain name service provider
To find the domain name service provider for your domain name
Windows Server
Open a web browser, and then type www.internic.com in the address bar to go to the InterNIC home page.
On the InterNIC home page, click Whois.
In the Whois box, type your domain name (for example contoso.com).
Click the Domain option, and then click Submit.
In the search results, the name of your domain name service provider is listed under Registrar.
Customize Remote Web Access
You can customize your Remote Web Access site by adding a personal logo or background image. You can also add links on the Home page so that this information is available to all of your users. For more information, see the following topics:
Customize Remote Web Access
You can customize Remote Web Access by changing the title of the website, changing the background image and logo, and adding links to other websites on the home page.
To customize Remote Web Access
Open the Dashboard.
Click Settings, and then click the Anywhere Access tab.
In the Web site settings section, click Customize.
When you finish customizing Remote Web Access, click OK. Test your changes on Remote Web Access.
Customize images for backgrounds and logos
This section provides information about the images that you can use to customize Remote Web Access.
Image size
Logo images
It is recommended that you use logo images that are 32x32 pixels. Larger images are shrunk to 32x32 and smaller images are stretched to 32x32, which could distort the image.
Background images
While there is no size limit for background images, for best results, it is recommended that you use images that are approximately 800x500 pixels. The background image is placed in the center (horizontal and vertical) of the logon page. To help make the text on the logon page easy to read, the center of the background image should be light in color.
Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Access Denied
Image file types
The following image file types can be used to replace the default background and website logo:
Bitmap (*.bmp, *.dib, *.rle)
GIF (*.gif)
PNG (*.png)
JPG (*.jpg)
Repair Remote Web Access
The Repair Wizard helps you detect and resolve problems with your router or domain name. There are two ways to discover issues with Remote Web Access:
Windows Server 2016 Remote Access Role

In Server Settings on the Dashboard, on the Anywhere Access tab, an icon is displayed with a red X along with a description of the issue.
An alert in the Alert Viewer.
Note
The Repair Wizard is not available until you turn on Remote Web Access. For information about turning on Remote Web Access, see Turn on Remote Web Access.
To repair Remote Web Access
Remote Access To Windows Server
Log on to the Dashboard.
Click Settings, and then click the Anywhere Access tab.
Click Repair. The Repair Remote Web Access Wizard starts.
Click Next. The wizard analyzes Remote Web Access, identifies the issue, and then attempts to repair the issue.
If you receive an alert when the wizard finishes, you can click Retry to try to repair the issue again. If you continue to receive an alert, check the alert for additional information about the issue and troubleshooting steps.
Enable Rdp On Server 2016
Troubleshoot Remote Web Access
Additional References
